Encapsulation in Java
Encapsulation in Java.
- Wrapping Private Data and bind the whole data and code as a single unit
- Hide Data, only can be access by the method of its current class.
How to Do Encapsulaion
- Declare the Variable as Private
- Create getter and Setter for the private Variable
Parent class the cars
package cars;
public class cars {
// Basic Car function
public int speeds;
// Create the Parent Class Constructor
public cars(int speeds) {
this.speeds = speeds;
}
// speeding is a Public Function , as you know all car Speed
public int increaseSpeed(int increase){
int result;
result =speeds +increase;
return result;
}
//decrease is a Public Function , as you know all car Speed decrease
public int decreaseSpeed(int decrease){
int results;
results=speeds -decrease;
return results;
}
//Check Horse Power
// auto Car
}
Child class audi
package cars;
public class audi extends cars {
int horsePower;
private String Patents =" This is the Audi Design know How";
public audi(int speeds,int horsePower) {
super(speeds);
this.horsePower= horsePower;
}
//************Inherited all this basic car function from cars class************
// Basic Car function
// speeding is a Public Function , all car Speed
//decrease speed
//******************************************************************************
// Child Class audi special Function
public void audiAuto(){
System.out.println("Audi is an AutoCar ");
}
//*****************Special Function only at this Class audi***************************************
public void checkHorsePower( int horsePower){
if (horsePower >1200){
System.out.println("Is a Big Car");
}
else{
System.out.println("Is a small Car");
}
}
//**********************Encapsulation Getter and Setter****************************************************
public String getPatents() {
return Patents;
}
public void setPatents(String patents) {
Patents = patents;
}
//*******************Calibrate Audi Performance Design******************************
//*******This Method can only be accesible within this Class****************
private void calibration(String cali ){
if(cali=="Y"){
System.out.println("Calibration Successful");
}
else{
System.out.println("Not calibrated");
}
}
}
Child class theCar
package cars;
public class theCar {
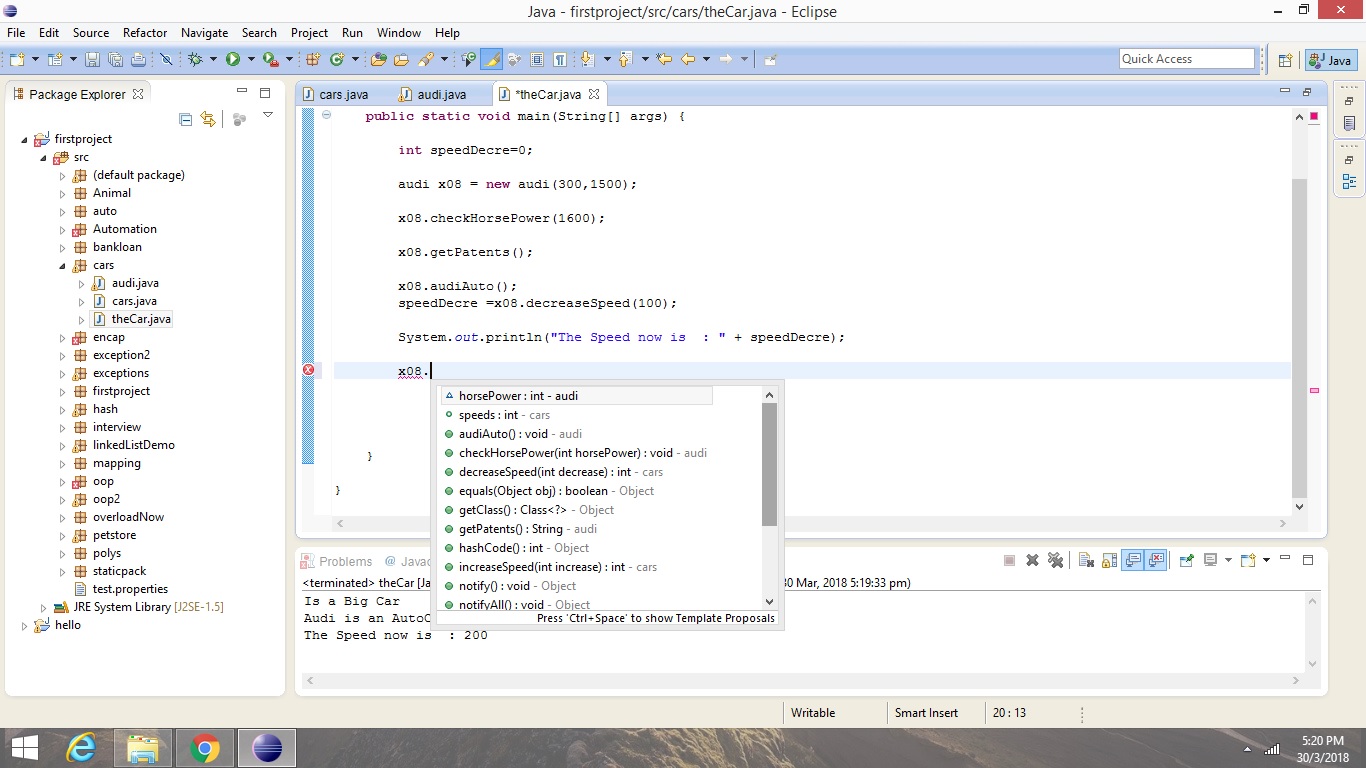
public static void main(String[] args) {
int speedDecre=0;
audi x08 = new audi(300,1500);
x08.checkHorsePower(1600);
System.out.println(x08.getPatents());
x08.audiAuto();
speedDecre =x08.decreaseSpeed(100);
System.out.println("The Speed now is : " + speedDecre);
}
}
Can’t access the calibration(String cali ) as this is only restricted in the audi class
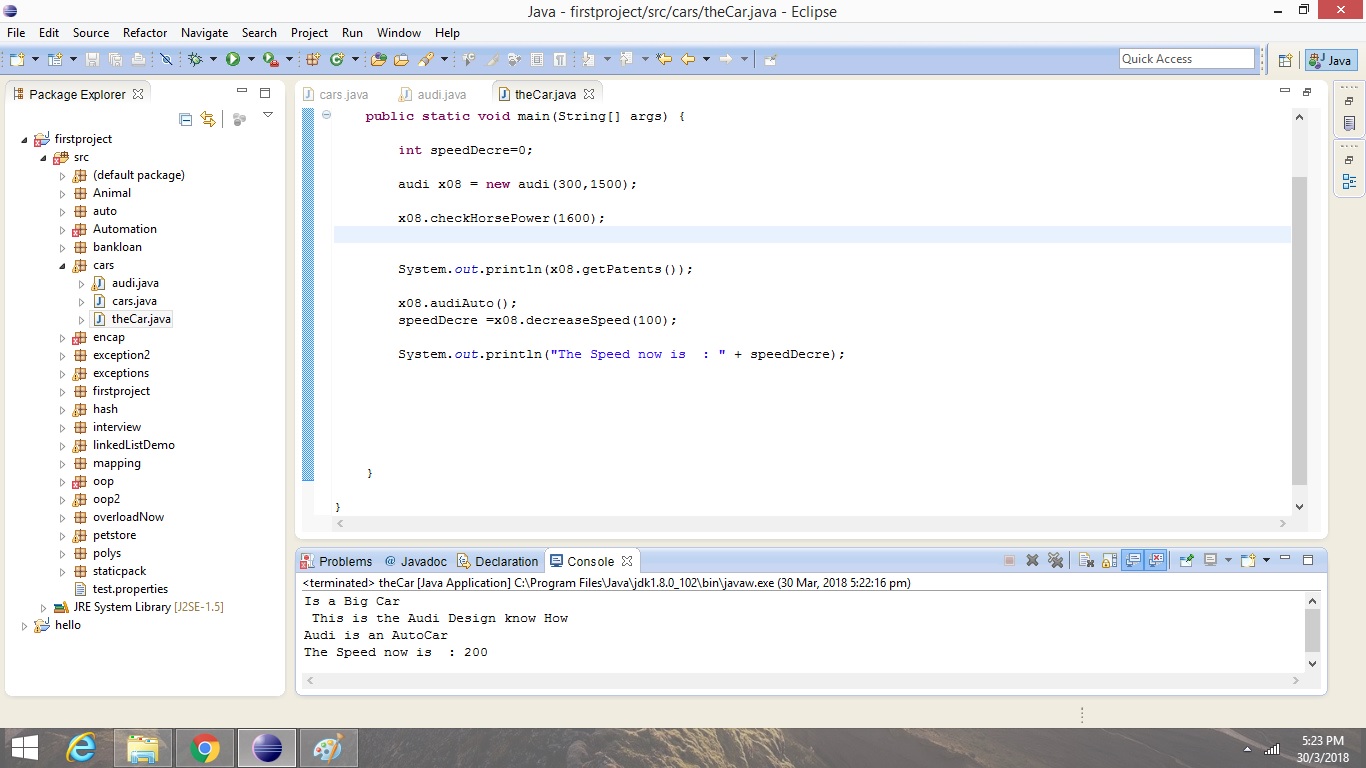
Output
Check out Polymorphism in Java here
Check out Oracle tutorial here
