Constructor in Java
Constructor in Java. In this Article we will look into our class and learn how to create a constructor.
What is a Constructor
| No | Constructor Features |
|---|---|
| 1 | A contructor is created automatically , when you did not create or declare a constructor specifically in your class. |
| 2 | Structure of the Constructor is similar to method , it will be called automatically when the class is created. |
| 3 | A Constructor can be Private or Public. If Public , the constructor will be able to be access by other constructor. |
| 4 | Constructor enable you to set a default or initial value in your Class. If a New Object is created it will overwrite the Constructor Default value. |
| 5 | Constructor can throw exception when un recoverable events happens . |
| 6 | You can create more than one Constructor in a class . |
| 7 | You can create more than one Constructor in a class . |
Constructor vs Method ( Constructor in Java)
| No | Attributes | Constructor | Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Called Automatically when a new Object is created | Yes | No |
| 2 | Considered as Member of a Class | No | Yes |
| 3 | Name of the Constructor must be same as the Class | Yes | No |
| 4 | Return Type | No | Yes |
| 5 | Created automatically in the System | Yes | No |
Lets Step into the Code and learn how to create a constructor in a class
In the example below , i will create 2 Class . The First Class i name it the “Dog” Class while the second class i name it “AccessDog” Class.The Dog class allows you to create a new object or instance for dogs.The AccessDog class function is to access the Dog Class.
Dog Class
- First , i created a Class name “Dog”
- 4 Private Variable which can only be accessible within this Class is Declare (dogname, dogbreed, dogcolor, dogAge)
- I set my first Constructor with the name “Dog ” as explain above the Constructor Name my be same and identical to the Class
- The first Constructor does not pass through any parameter through its parentheses
- I have set some default value inside my First Constructor
- I Set my second Constructor which allow User to Pass through Parameter through its Paratheses
- this.dogname= dogname;means, to assign the value in public Dog(String dogname ,String dogbreed, String dogcolor ,int dogAge)
into private String dogname; - The Remaining code below shows how to code the setter and the getter for the class. Refer here on how to code the Setter and Getter.
package oop2;
public class Dog {
private String dogname;
private String dogbreed;
private String dogcolor;
private int dogAge;
public Dog(){
this.dogname = "wangwang";
this.dogbreed = "labrador";
this.dogcolor = "brown";
this.dogAge = 2;
}
public Dog(String dogname ,String dogbreed, String dogcolor ,int dogAge){
this.dogname= dogname;
this.dogbreed=dogbreed;
this.dogcolor=dogcolor;
this.dogAge=dogAge;
}
public String getDogname() {
return dogname;
}
public void setDogname(String dogname) {
this.dogname = dogname;
}
public void setDogBreed(String dogbreed){
this.dogbreed = dogbreed;
}
public String getDogBreed(){
return this.dogbreed;
}
public String getDogcolor() {
return dogcolor;
}
public void setDogcolor(String dogcolor) {
this.dogcolor = dogcolor;
}
public int getDogAge() {
return dogAge;
}
public void setDogAge(int dogAge) {
this.dogAge = dogAge;
}
}
AccessDog Class
- Now we have finished our Dog class lets create our AcessDog Class
- To use the Scan Function i will need to import java.util.*;
- Declare 4 Static Variable to be Use later below in the program
- Declare 4 new Scanner Object call inputScan1, 2,3,4
- Create a new Dog name called origin using the Default Constructor
- called the Getter method of the dog class to print out the Default Value
- Print out the Statement to request the user to input the Dog name
- inputDogname = inputScan1.nextLine(); Assign the value the user key in the Scanner object named inputScanner1 into the inputDogname variable
- Same apply to the remaining below
- Dog inputDog =new Dog(inputDogname,inputBreed,inputColor,inputAge); Assign the User input into the second constructor that we created
- System.out.println(inputDog.getDogname()); Access the Dog Class Getter and print out all the Dog attributes that the User have enter just now
- Close all the Scanner Objects.
package oop2;
import java.util.*;
public class AccessDog {
static String inputDogname;
static String inputBreed;
static String inputColor;
static int inputAge;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner inputScan1 = new Scanner(System.in);
Scanner inputScan2 = new Scanner(System.in);
Scanner inputScan3 = new Scanner(System.in);
Scanner inputScan4 = new Scanner(System.in);
Dog origin =new Dog();
//Print the Default Dog name
System.out.println(origin.getDogname());
System.out.println(origin.getDogBreed());
System.out.println(origin.getDogcolor());
System.out.print(origin.getDogAge());
System.out.println("Input Your Dog Name ?");
inputDogname = inputScan1.nextLine();
System.out.println("Input Your Dog Breed ?");
inputBreed = inputScan2.nextLine();
System.out.println("Input Your Dog Color ?");
inputColor= inputScan3.nextLine();
System.out.println("Input Your Dog Age ?");
inputAge =inputScan4.nextInt();
//Input all value into the Constructor
Dog inputDog =new Dog(inputDogname,inputBreed,inputColor,inputAge);
System.out.println(inputDog.getDogname());
System.out.println(inputDog.getDogBreed());
System.out.println(inputDog.getDogcolor());
System.out.print(inputDog.getDogAge());
inputScan1.close();
inputScan2.close();
inputScan3.close();
inputScan4.close();
}
}
Results as shown below
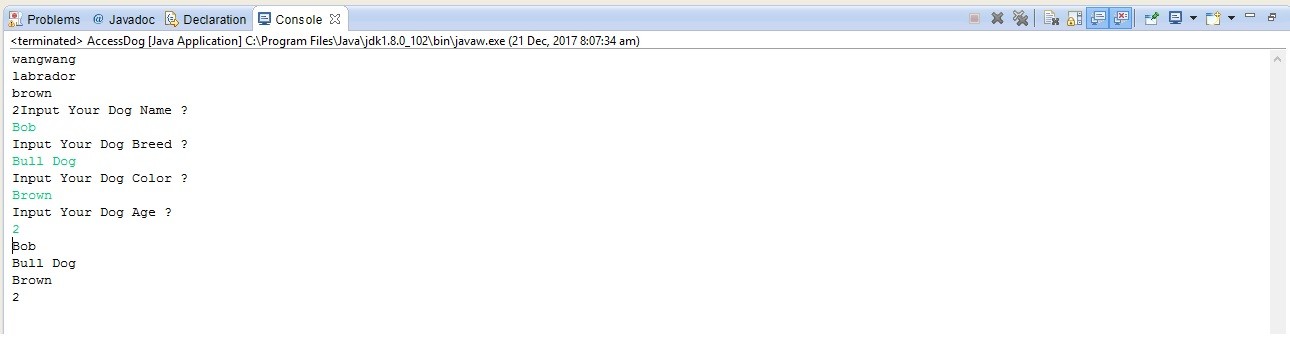
Well this Wrap up the article about Constructor in Java.
Check out here for more information about Constructor.
